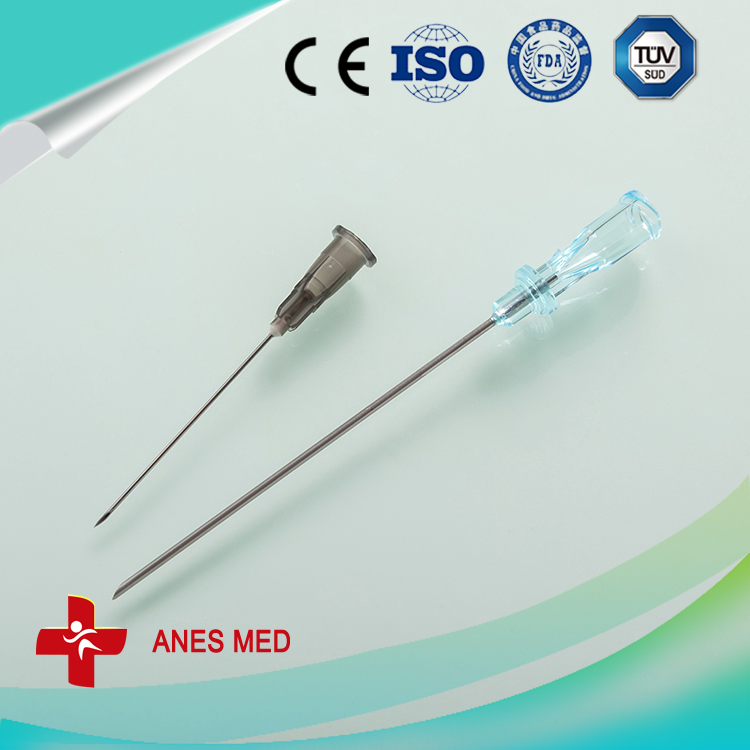
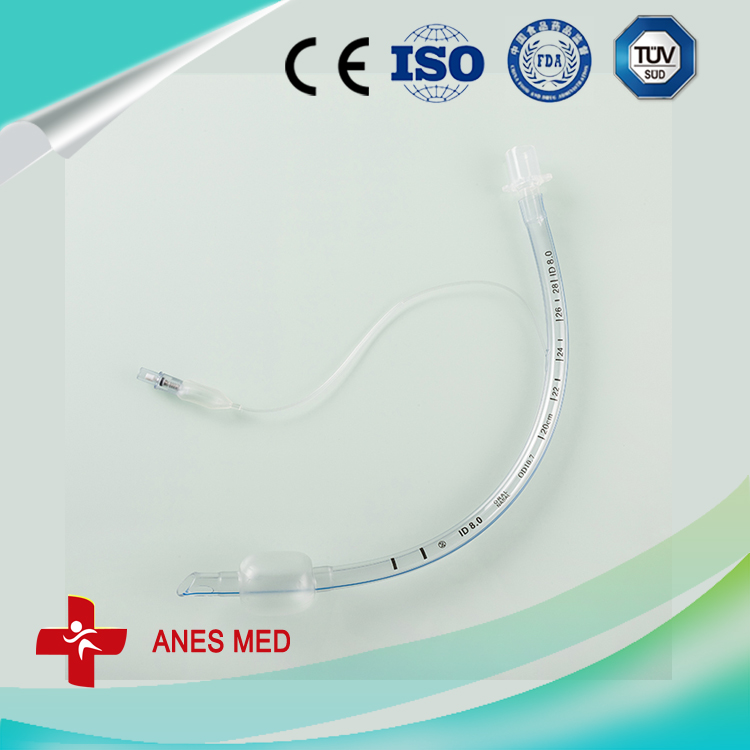
pidural and spinal combined anesthesia puncture, Epidural Needle ,Introducer Needle, Infusion Pumps ,trachea cannula,
Components FOR AS-E/S FULL KIT
(AS-E/S) Combined spinal Epidural Anesthesia puncture package/kit
Y-valve Connector
Epidural Needle,Introducer Needle,Infusion Pumps,Tracheal Cannula,Y-valve Connector,Blood Inflation Balloon Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , http://www.sinoanesthesia.com
Therefore, when indirect methods are used to measure IgM antibodies, serum samples are usually pretreated with anti-human IgG antibodies or SPA to remove IgG interference. This is not only cumbersome to measure, but also affects the specificity and sensitivity of the assay. At present, the commonly used IgM antibody detection method is a capture method, that is, an anti-human IgM antibody (anti-human u chain) is used as a solid phase antibody, and when a serum sample is added, an IgM type antibody (specific and non-specific) can be used. After being captured by the solid phase antibody, a specific antigen is added, and after binding to the IgM antibody captured on the solid phase, an antibody against the specific antigen is added, and the substrate is added to develop color. The specific steps are as follows:
1. First, the anti-human IgMbt chain antibody was coated with a solid phase such as polystyrene in a carbonate buffer at 40 c overnight to form a solid phase antibody, and the antibody which was not bound to the solid phase or which was not tightly bound was removed by washing, and the calf serum was used. Or bovine serum albumin or the like is blocked, and the unbound portion and impurities are removed by washing.
2. A clinical sample containing the IgM antibody to be tested, such as serum, is added, and the plate is washed after a certain period of time; at this time, the IgM antibody in the sample to be tested reacts with the anti-P chain antibody on the solid phase to adsorb on the solid phase.
3. A specific antigen such as HAV antigen, HBcAg, or the like is added, and the plate is washed after a certain period of incubation; at this time, the specific antigen reacts with the specific IgM antibody on the solid phase.
4. The enzyme-labeled antibody against the specific antigen is added, and the plate is washed after a certain period of incubation; at this time, the corresponding antigen-antibody complex is formed on the solid phase.
5. The enzyme substrate was added and the color development assay was incubated.
This method should pay attention to the interference of RF (1gM class) and other non-specific IgM. RF (class 1gM) is capable of reacting with a solid phase anti-human u-chain antibody and can react with a subsequently added enzyme-labeled antibody (animal IgG), resulting in a false positive reaction. Non-specific IgM can compete with specific IgM for binding to solid-phase antibodies due to its in-step incubation, thus affecting the sensitivity of the assay. Therefore, to measure IgM using this method, clinical samples must be properly diluted. After the sample is diluted, the above-mentioned non-specific IgM content that causes interference is reduced, and the specific IgM is in the acute infection period of the corresponding pathogen, the titer is high, and after dilution, there is no significant influence. Moreover, in some pathogens such as HBV In the chronic infection phase, IgM-specific antibodies can persist, but the titer is much lower.
Therefore, if the serum sample is not diluted, it is directly detected, and even if there is no interference of non-specific IgM, the positive measurement result has no diagnostic value of acute infection. Nowadays, some reagent manufacturers have produced anti-HAVIgM and anti-HBclgM ELISA kits that do not need to dilute the samples in order to meet the requirements of clinical laboratories to reduce labor intensity and ease of operation. Many laboratories are also in use. For the reasons mentioned above, we recommend that clinical laboratories use a kit that dilutes the sample when performing anti-HAVIgM and anti-HBclgM tests to ensure the clinical value of the test.
Name
Spec.
Qty.
Epidural needle
16G
1
spinal needle
25G
1
No damage Anesthesia
Catheter (Patent)
length>90cm
OD 1.0mm
1
Anesthesia catheter adapter
--
1
Air filter
-
1
Liquid filter
-
1
Catheter assist guide
-
1
Surgical latex gloves
7.0# 7.5# 8#
1
Negative pressure tube
-
1
Sponge brush
3
Sterile injector needle
16G 1.6
1
22G 0.7
1
23G 0.6
1
Low-resistance injector
5ml
Sterile syringe
20ml
1
3ml
1
Woundplast
-
1
Compresses
7*7*8
3
Tray cover
-
1
Catheter adhesive slice
5cm*8cm
1
Bottom cover
-
(AS-E) Epidural anesthesia puncture package/kit
(AS-S) Spinal anesthesia puncture package/kit
(AS-N) Nerve Anesthesia puncture package/kit
Blood Inflation Balloon

A Common Mode of ELISA Assay--IgM Antibody by Solid Phase Capture Method
In the diagnosis of pathogen acute infection, it is usually necessary to detect IgM antibodies, such as serum anti-HAVIgM test for acute hepatitis A diagnosis, serum anti-HBclgM test for acute hepatitis B virus infection, and serial IgM test for TORCH project. IgM antibodies are also assayed using indirect methods, such as some of the TORCH series of IgM assay kits currently available on the market. When the IgM antibody is detected by the indirect method, since the clinical serum sample contains a high concentration of IgG antibody, some of the specific IgG antibodies will compete with the IgM antibody for binding to the solid phase antigen, thereby interfering with the detection of the IgM antibody.
